First Trip Testing Using the PKV/M7 Analyzer Measurement of Real-Life Time of Circuit Breaker Operation
Depending on the HV circuit breaker type (oil, air, SF6, or vacuum), a list of measured characteristics used for assessing its technical condition can be different. According to standardization documentation, along with the measurement of the main parameters there exist a number of other tests that give additional information on the equipment serviceability. First trip testing or measurement of real-life time of circuit breaker opening is one of currently actively developed methods.
As early as in 1963 a book "Operation and Maintenance of Electromagnetic Drives of HV Circuit-Breakers" was published under aegis of the State Production Committee on Energy and the USSR Electrification. The book stated that time of HV circuit breaker opening (that has been inactive for a long time) is affected by such factors as:
- lubrication problems (hardened grease) of a drive;
- grease hardening due to dust sticking;
- rusting of drive elements due to condensate occurrence and drying;
- chemical interaction of grease with protected elements (due to incorrect grease selection);
- condensate freezing in different joints (especially in conditions of Siberia and the Extreme North);
- deterioration of greasing properties due to mixing of different materials, etc.
In case of a short circuit the above factors may slow the HV circuit breaker operation, which may result in:
- damage or rapid wear of the arch extinguishing chamber contact due to long burning of the arch;
- burnout of TRIPPING coils due to slow operation of the circuit breaker's block-contactor that leads to long-term current flow let through;
- operation of a HV circuit breaker of higher voltage class that leads to disconnection of a large group of consumers instead of one consumer;
- needless re-adjustment of PSP, etc.
It is important to know how fast the breaker will open after having been left close for a year or longer. Scheduled repair or maintenance of a breaker, or its multiple close/opening brings the time of circuit breaker operation back to normal. Therefore, during regular maintenance the problems of this particular circuit breaker can be easily overlooked.
One of the most reliable methods of measuring the circuit breaker opening time in real operation (after being in closed position for a long time) is direct measurement of current flow time through the opening solenoid during scheduled outage of a circuit breaker.
Key idea of the method is that displacements of the main contacts and block-contacts of drives in the oil, low-oil and some types of SF6 and vacuum circuit breakers are closely related. Therefore, increased time of block-contacts opening is an evidence of increased time of the main contacts opening.
Measurement of current flow time through the opening solenoid is the most convenient method of assessing the main contacts opening time at first tripping. According to "Scope and Standards of Electric Equipment Testing" (RD 34.45-51.300-97), measurement of open/close pulse time is mandatory. Therefore, the user can compare the first tripping time of current impulse with the tripping time measured during the last test of the circuit breaker performances.
Technique of the first trip testing using the PKV/M7 instrument and current clamps (provided upon order) is as follows:
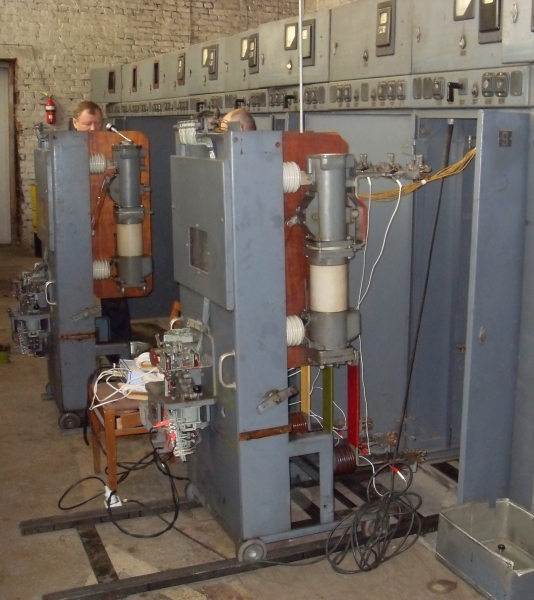
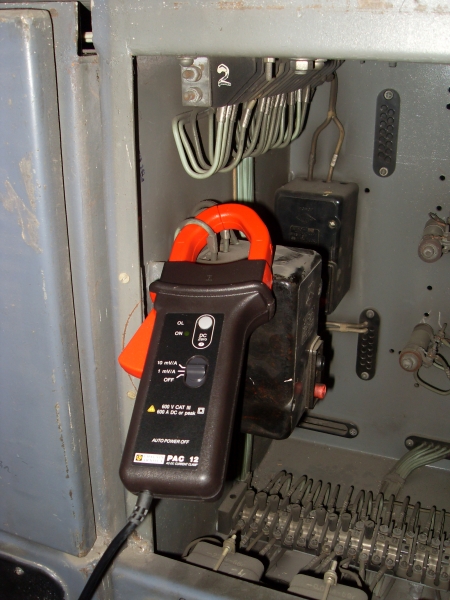
- Connect the current clips, i.e., embrace one of the conductors of the operating current circuit with magnetic wire of the clips (Fig. 1).
- Adjust the analyzer to the local start-up.
- Specify the time of measurement (5.1 s).
- Turn the analyzer over to the "startup wait" mode.
- Against the STARTUP command one of the crew members starts up the analyzer for measurements, then the second member of the crew turns the circuit breaker control switch to the OPEN position (time allowed between the analyzer startup for measurements and a command for circuit breaker opening is 5 s).
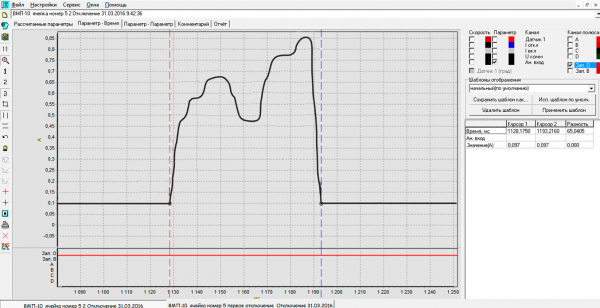
- After termination of measurements the analyzer is turned over to the mode of plotting the current graph, and the current pulse time is measured using the two cursors (Fig. 2).
This technique was tested during scheduled maintenance of one of the VMPE-10 circuit breaker cubicles.
Fig. 1. VMPE-10 circuit breaker. Place for connecting the current clamps of the PKV/M7 analyzer.
Opening time of the main contacts measured during scheduled maintenance more than a year ago was 73.2ms, current pulse time was 61.2ms.
Results of the first trip test performed a year after the last scheduled test of a circuit breaker were as follows: time of the opening solenoid current pulse was 65ms, which was approximately 6% higher than the value obtained a year ago. Hence, while the circuit breaker was in closed mode, the opening time of the main contacts increased approximately by 6% (presumably due to negligible grease drying), which equals 73.2мс + 6% = 77.6ms.
According to VMPE-10 circuit breaker passport data, opening time proper shall not exceed 100ms. Thus, despite longer time of the main contacts opening, real-life time of the circuit breaker opening in case of an unexpected short circuit will be within the norm and will not lead to equipment wear in emergency situation.
Fig. 2. Graph of the pulse of current flowing through the operating current circuits at the moment of tripping.
The first trip test function in the PKV/M7 analyzer is optional one. The analyzer allows solution of other tasks related to control and diagnosis of the HV circuit breakers of both Russian and foreign manufacture (ABB, Areva, Siemens, Alstom, and others). The method of recording speed, travel and time characteristics implemented in the instrument allows off-line testing of breakers. For example, for the case of the oil circuit breakers the OPEN/CLOSE operations are performed without oil drainage; controlled parameters are capable of giving the overall idea on the circuit breaker state.
 Moreover, the instrument is capable of plotting the graphs of functions, which, unlike tabular presentation, vividly show operation of each elements of a circuit breaker. Automatic overlapping of dependences for each pole allows identification of such heavy faults as, for example, clearances in the pole mechanisms, that is of special importance for circuit breakers with one drive for three phases, as this fault cannot be identified using numerical values only.
Moreover, the instrument is capable of plotting the graphs of functions, which, unlike tabular presentation, vividly show operation of each elements of a circuit breaker. Automatic overlapping of dependences for each pole allows identification of such heavy faults as, for example, clearances in the pole mechanisms, that is of special importance for circuit breakers with one drive for three phases, as this fault cannot be identified using numerical values only.
According to references of users, the PKV/M7 analyzer both reduces the time of the circuit breaker testing (the time of measurements is as low as 5-10 minutes) and the number of operations needed for testing.
If you have got interested in the PKV/M7 analyzer and you want to know more about the HV circuit breaker analyzers, and the first trip method procedure, do not hesitate to contact our managers by the telephone: +7 (3952) 719-148 or by email: skb@skbpribor.com.

 Русский
Русский
 Français
Français
 Chinese
Chinese